Yarn Design
1. Linear density of spinning yarn
Determination of the linear density of spinning yarn is one of the main contents of fabric design. The linear density plays a decisive role in the performance of the fabric and should be selected according to the use and characteristics of the fabric.
In fabric design, there are generally three forms of configuration of warp and weft density, namely Ttj=Ttw, Ttj>Ttw, Ttj<Ttw. In most cases, the two forms Ttj=Ttw and TtjTtw is also adopted. If the density of warp and weft threads is different, the difference should not be too large. Because the density difference between warp and weft lines is too large, it will change the geometric structure of the fabric, change the buckling of warp and weft yarns, change the state of the spinning yarn as the supporting surface on the fabric, and affect the wear resistance and other wearing properties of the fabric.
2. Twist of spinning yarn
The twist of spinning yarn is related to the appearance and fastness of the fabric. When designing, certain requirements should be put forward for the twist of spinning yarn according to the characteristics of the fabric. Within the critical twist range, appropriately increasing the twist of spinning yarns can improve the strength of the fabric. However, if the twist is too large, the fabric will feel stiff and have a weak finish. Fabrics with smaller twist will have a softer feel and better finish. During the design process, different twist coefficients should be selected according to the different warp and weft yarns and fiber lengths in the fabric. Generally, the twist of warp yarn is slightly higher than that of weft yarn, the twist of thin fabric is greater than that of medium-thick fabric, the twist of tight fabric is greater than that of soft fabric, the twist of spinning yarn with low linear density is greater than the twist of spinning yarn with high linear density, and the twist of spinning yarn with short fiber length is The twist of a spinning yarn is greater than the twist of a spinning yarn with a long fiber length.
When the fabric is woven with strands, the twist combination of the thread and yarn has a certain impact on the fabric’s strength, wear resistance, finish, and feel.
When the ratio of twist coefficients between strands and single yarns is √2, the strands have high strength. When the ratio of twist coefficients is 1, the surface fibers are parallel to the axis of the strands, and the spinning yarn is in good condition, and Spun yarn has a tighter structure. Since some impurities have been removed from the single yarn during the twisting process, and the surface hairiness is reduced, the wear resistance, feel and finish of the thread fabric are better than those of the yarn fabric.
3. The twist direction of the spinning yarn and the reverse belt on the floating section of the spinning yarn
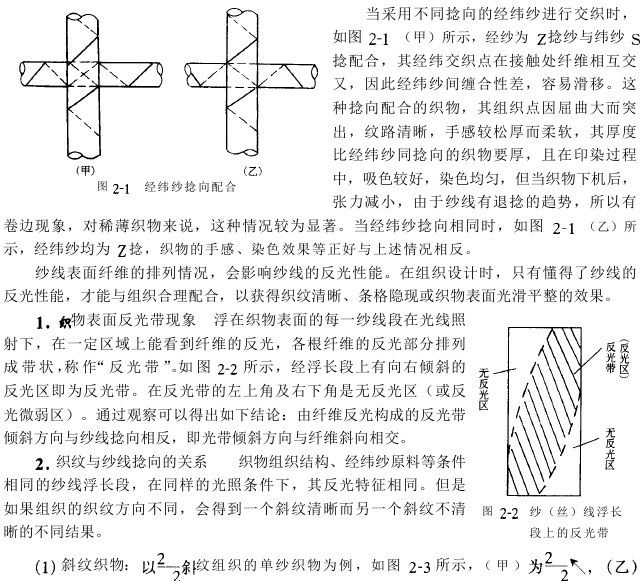
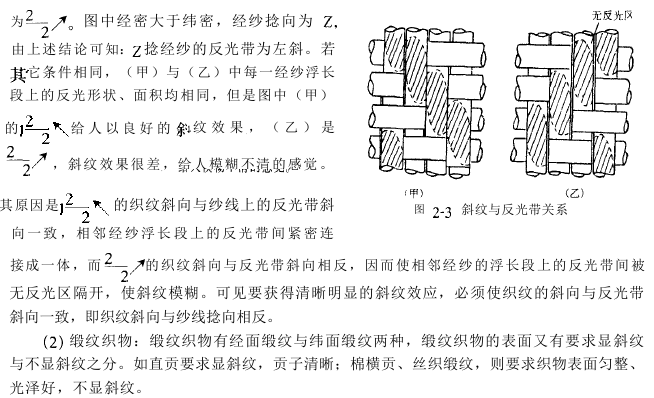
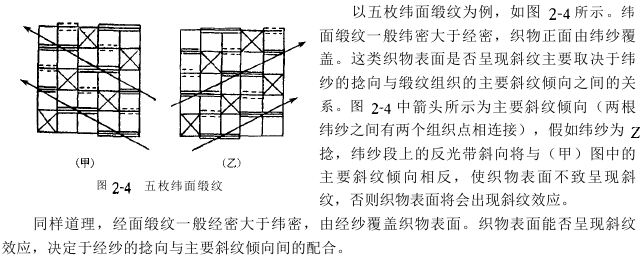
The twist direction of the spinning yarn is divided into two types: Z twist (right twist) and S twist (left twist). The fabric The combination of the twist direction of the mid-warp and weft yarns has a certain impact on the feel, thickness, and surface texture of the fabric. Usually there are four forms of combination of warp and weft yarn twist directions, namely, Z-twist warp yarn and Z-twist weft yarn, S-twist warp yarn and S-twist weft yarn in the same twist direction, Z-twist warp yarn and S-twist warp yarn, S-twist warp yarn and Z-twist weft yarn. Matching with different twist directions.
AAADF3RSEGDTHIU





